Groundwater extraction for agricultural purposes is a widespread practice that plays a critical role in ensuring food security for communities across the world. Groundwater is a valuable resource for agriculture because it provides a reliable source of irrigation water even during periods of drought. However, excessive extraction of groundwater can lead to declining water levels, which can impact the sustainability of the resource and the health of aquatic ecosystems.
Agriculture is the largest consumer of water globally, accounting for approximately 70% of total water use. In many areas, surface water resources are unreliable or insufficient for meeting the needs of agriculture, making groundwater extraction an important alternative. Groundwater can be a more reliable source of water for irrigation, especially in areas with low rainfall or high-water demand.
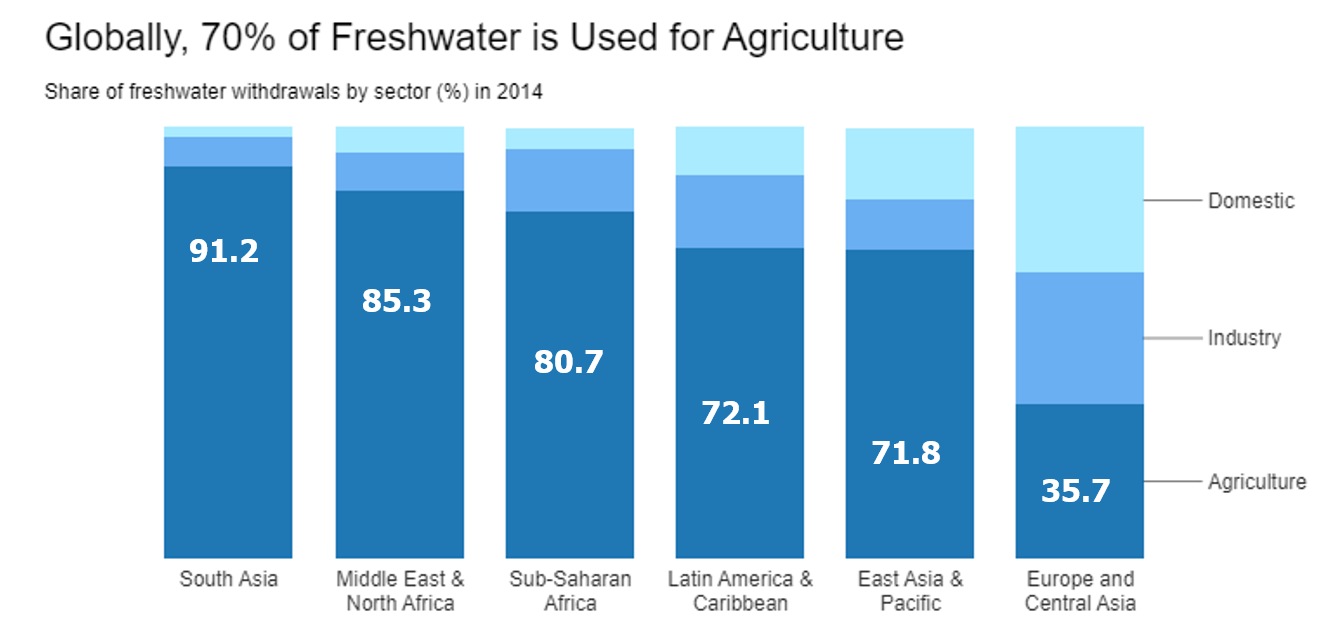 Figure 1: Freshwater used for Agriculture (Source: World Development Indicators)
Figure 1: Freshwater used for Agriculture (Source: World Development Indicators)
Excessive groundwater extraction for agriculture can have several impacts on the environment and communities. The primary impact is declining water levels, which can lead to reduced availability of water for agriculture and other uses. This can result in lower crop yields, reduced income for farmers, and higher food prices. Additionally, declining water levels can impact the health of aquatic ecosystems, such as streams and rivers, by reducing the amount of water available for these systems to function.
Groundwater is an important source of irrigation for agriculture in Bangladesh. The country is facing severe water scarcity due to over-extraction of groundwater, which is leading to a decline in the water table and decreased crop yields. The decline in the water table has led to the increased salinity of groundwater, making it unsuitable for irrigation purposes. The increased salinity of groundwater is also affecting the soil fertility, leading to decreased crop yields.
To ensure sustainable use of groundwater for agriculture, it is important to implement effective management strategies. These strategies can include:
Groundwater extraction for agriculture plays a critical role in ensuring food security for communities across the world. In Bangladesh groundwater extraction is contributing to the decline of groundwater resources in the country. The over-extraction of groundwater is leading to a decline in the water table, increased salinity of groundwater, decreased crop yields, and decreased food production. However, excessive extraction of groundwater can have negative impacts on the environment and communities. It is important to implement sustainable groundwater management practices to ensure the long-term sustainability of groundwater resources in Bangladesh.
Major data sources and interactive maps for the groundwater and agriculture:
These sources can provide valuable information on groundwater extraction for agriculture and can be useful for research, policymaking, and resource management.
This website was produced with the support of the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) under the terms of USAID's Research for Decision Makers (RDM) Activity cooperative agreement no. AID-388-A-17-00006
Views expressed herein do not necessarily reflect the views of the U.S. Government or USAID. icddr,b is also grateful to the Governments of Bangladesh, Canada, Sweden and the UK for providing unrestricted/institutional support
68, Shaheed Tajuddin Ahmed Sarani Mohakhali, Dhaka 1212, Bangladesh
icddr,b is located at the Mohakhali area in Dhaka, just ask your driver for the "Cholera Hospital"
